In C programming, variables or memory locations should be declared before it can be used. Similarly, a function also needs to be declared before use.
Data types simply refers to the type and size of data associated with variables and functions.
Data types in C
- Fundamental Data Types
- Integer types
- Floating type
- Character type
- Derived Data Types
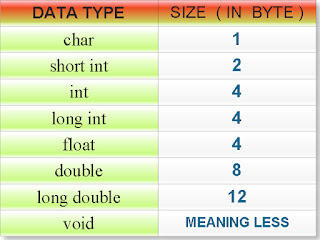
size chart of various data types
we can understand the classification of data types using the following diagram:
Integer data types
Integers are whole numbers that can have both positive and negative values, but no decimal values. Example: 0, -5, 10
In C programming, keyword int is used for declaring integer variable. For example:
int id;
Here, id is a variable of type integer.
You can declare multiple variable at once in C programming. For example:
int id, age;
The size of int is either 2 bytes(In older PC's) or 4 bytes. If you consider an integer having size of 4 byte( equal to 32 bits), it can take 232 distinct states as: -231,-231+1, ...,-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ..., 231-2, 231-1
Similarly, int of 2 bytes, it can take 216 distinct states from -215 to 215-1. If you try to store larger number than 231-1, i.e,+2147483647 and smaller number than -231, i.e, -2147483648, program will not run correctly.
Floating types
Floating type variables can hold real numbers such as: 2.34, -9.382, 5.0 etc. You can declare a floating point variable in C by using either float or double keyword. For example:
float accountBalance; double bookPrice;
Here, both accountBalance and bookPrice are floating type variables.
In C, floating values can be represented in exponential form as well. For example:
float normalizationFactor = 22.442e2;
Difference between float and double
The size of float (single precision float data type) is 4 bytes. And the size ofdouble (double precision float data type) is 8 bytes. Floating point variables has a precision of 6 digits whereas the precision of double is 14 digits.
Character types
Keyword char is used for declaring character type variables. For example:
char test = 'h'
Here, test is a character variable. The value of test is 'h'.
The size of character variable is 1 byte.
C Qualifiers
Qualifiers alters the meaning of base data types to yield a new data type.
Size qualifiers
Size qualifiers alters the size of a basic type. There are two size qualifiers, longand short. For example:
long double i;
The size of float is 8 bytes. However, when long keyword is used, that variable becomes 10 bytes.
If you know that the value of a variable will not be large, short can be used.
Sign qualifiers
Integers and floating point variables can hold both negative and positive values. However, if a variable needs to hold positive value only, unsigned data types are used. For example:
// unsigned variables cannot hold negative value unsigned int positiveInteger;
There is another qualifier signed which can hold both negative and positive only. However, it is not necessary to define variable signed since a variable is signed by default.
An integer variable of 4 bytes can hold data from -231 to 231-1. However, if the variable is defined as unsigned, it can hold data from 0 to 232-1.
It is important to note that, sign qualifiers can be applied to int and char types only.
Constant qualifiers
An identifier can be declared as a constant. To do so const keyword is used.
const int cost = 20;
The value of cost cannot be changed in the program.
Volatile qualifiers
A variable should be declared volatile whenever its value can be changed by some external sources outside the program. Keyword volatile is used for creating volatile variables.
for next topic visit : rawsoftwares.blogspot.com


No comments:
Post a Comment